Solar vs Gas Generator
Updated:

When it comes to solar generator vs gas generator, multiple factors come into play in the face-off between these two types of generators.
Solar-powered generators utilize the sun’s energy, offering an eco-friendly, low-maintenance solution with potentially lower long-term costs.
In contrast, gas-powered generators deliver immediate, consistent power output regardless of weather conditions but have higher operational costs and environmental concerns.
This article presents these contrasts, giving a comprehensive overview of both.
Solar Generator vs. Gasoline Generator: A Comprehensive Comparison
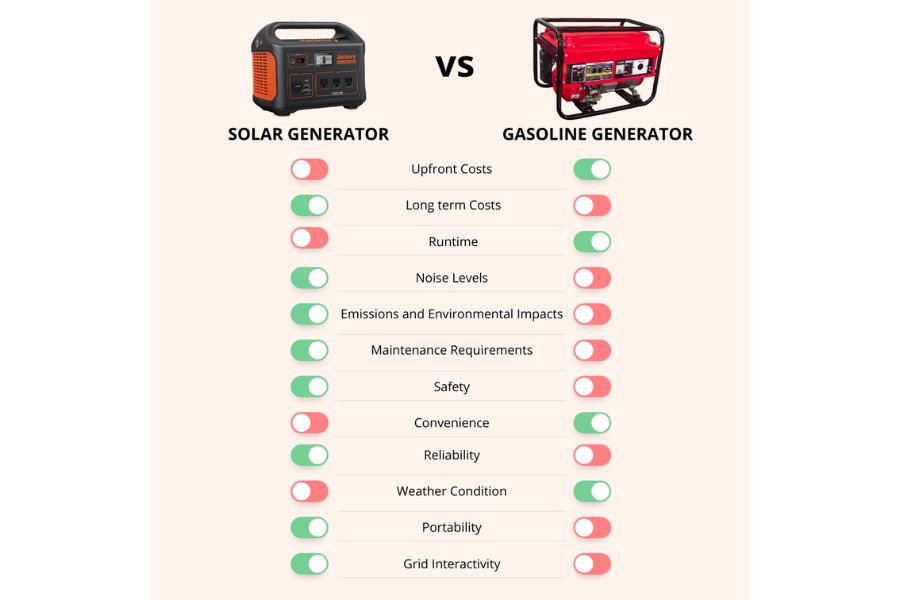
Choosing between solar and gasoline generators involves more than upfront costs and eco-friendliness. Let’s define their differences across key parameters to guide your decision.
Upfront Costs
Solar power systems cost a lot more upfront than regular gas generators.
If you’re looking at a basic gas generator that produces 1,000 watts of power, you might pay between $300 and $500. But, the starting price for a solar system, which includes a 600-watt power machine and a 100-watt solar panel, is usually $800 or even more.
This sizable upfront price tag for solar generators includes more than just the cost of solar panels. It also includes the expense of lithium batteries, inverter, solar charge controller, cables, mounts, and electronics.
Gas generators are simpler. They mostly have a tank for the fuel, an engine, a machine to produce electricity, and a few controls. So, they need fewer parts, which makes them cheaper.
But, if you’re in the US, there’s some good news. The government offers tax breaks to help with the cost of solar systems. There’s a tax program called the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC). If you buy a solar system between 2023-2032, you get a tax break of 30%.
Considering these savings, solar systems can cost closer to what gas generators do.
Long-Term Costs
Solar generators, when in operation, can save you a lot on fuel costs in the long run compared to gas-powered generators. Once you buy a solar generator, it can give you free electricity for 15-25 years if you take good care of it. This means you get free renewable energy for many years because of solar panels.
On the other hand, gas generators use a lot of fuel when running, which can get expensive. For example, a 2,500-watt gas generator might use up to a gallon of gas in an hour when running a lot of devices. In the US, gas costs about $3.6 for a gallon. So, every hour you use the gas generator, it could cost you between $1.8 and $3.6.

Let’s say there’s a power cut, and you use the gas generator for 10 hours. Just for that day, you might spend $18-$36 on fuel alone. Over many days and years, this can become a significant expense.
Runtime
Gas-powered generators can work non-stop for long periods. They only need to pause when they run out of fuel.
Fortunately, the refueling process is straightforward and can be completed in just a few minutes, ensuring an uninterrupted power source for longer. Failures can be handled by rationing energy and combining both generator technologies.
On the other hand, solar generators provide a reliable power source during daylight hours. As long as the sun shines, these generators continuously charge their batteries and operate.
Most solar generators have batteries at night that can provide power for 5-10 hours. The power supply can last for days for those with larger battery capacities, making it a sustainable choice for many.
Noise Levels
Gasoline generators make quite a bit of noise. This sound arises primarily because of their engine and the moving parts inside. When these generators run, their loudness can be somewhat disruptive, especially if you’re nearby.
In contrast, solar generators offer a much quieter experience. Their design, which incorporates silent cooling fans, ensures they operate with minimal disturbance. Even when standing close, they emit barely audible sounds. This whisper-like operation makes solar generators suitable for indoor use, guaranteeing a peaceful ambiance.
Emissions and Environmental Impacts
Gasoline generators release substantial emissions from burning fossil fuels, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbon compounds. These harmful emissions contribute to air pollution.
Solar generators, on the other hand, use renewable energy sources. They are emissions-free and run solely on solar power, making them much better for the environment.
Maintenance Requirements
Gasoline generators have many parts like the engine, muffler, fuel system, starter, air filter, etc. These parts need regular checking and sometimes replacement to keep the generator working well.
On the other hand, solar generators mostly need their panels cleaned from time to time. Their design is simpler and doesn’t have many moving parts, which makes them easier to maintain. The main thing you might need to do is replace the batteries about every 5-10 years.
Safety
Gasoline generators are powered by flammable fuels, presenting a clear fire danger. This risk arises from potential leaks, fumes, and stray sparks.
These generators also produce harmful exhaust, increasing the danger of carbon monoxide poisoning. It’s best to operate them outdoors and away from windows for safety.
Solar generators operate using lithium batteries, which are inherently safe and devoid of dangerous fumes or flammable elements. This makes them a reliable choice for both indoor and outdoor use.
However, it’s essential to ensure they remain dry to prevent any potential water damage.
Convenience
Gasoline generators provide power on demand as soon as they’re fueled. With auto-start features, a simple button press can activate them, instantly offering power. This quick response makes them handy during emergencies.
Solar generators take more foresight and planning to extract their full potential. The sun only shines during the day, so charging takes advanced preparation.
Solar panels must also be pointed in the proper direction each day. However, they operate effortlessly once everything’s in place and offer consistent energy.

Reliability
Solar generators are highly durable and reliable, with 15-25 years of lifespan. Only the batteries need replacement every 5-10 years. Solar generators work indefinitely with proper care and maintenance as long as sunlight is available. Their solid-state components are not subject to mechanical failure.
On the other hand, gasoline generators come with a comparatively shorter lifespan. This is mainly due to wear and tear on their internal components. Storing them without proper care can result in fuel residue buildup, affecting performance.
Additionally, if there’s a fuel supply disruption, these generators can’t function. Their design, with several moving parts, often requires repairs and consistent maintenance.
Solar generators have the upper hand during grid failures, working effectively if their batteries have a charge. In contrast, gas generators require a steady fuel supply, which might be unavailable during crises.
While gasoline generators demand continuous monitoring for peak performance, once set up, solar ones can operate without any oversight, making them a more dependable choice.
Weather Condition
Solar generators need clear, sunny skies to perform at their best. Their output can drop when faced with cloudy conditions, shorter daylight during winter, or weather disruptions like rain or snow.
Users must plan and manage their battery reserves wisely to ensure a steady power supply, especially during such times. Monitoring weather forecasts and charging batteries ahead of predicted bad weather is crucial. Essentially, their performance varies based on environmental factors.
Gasoline generators, in contrast, can offer a steady power supply under a broader range of conditions. Rain, clouds, or a lack of sunlight don’t affect them as much. They can consistently provide their rated power as long as they’re fueled.
Cold conditions are a notable exception, as they can hinder fuel combustion and performance. However, gasoline generators stand out outside extreme temperatures as dependable power sources with fewer environmental restrictions.
Portability
Solar generators, often called portable power stations, are favored for their portability. Their design is compact and lightweight, often integrating solar panels, batteries, and inverters in a single unit.
This design simplicity, combined with features like carrying handles or wheels, makes them ideal for various activities. Whether camping, a road trip, or just storage in tight spaces, these portable solar generators easily fit the bill.
Gasoline generators are notably heavier and larger, with their robust steel frames and sizable engines adding to the weight. This makes transporting them more cumbersome, often requiring careful planning and extra help.
The addition of external fuel tanks or storage necessities further complicates their mobility. These factors make them less convenient for activities like camping or stowing away in vehicles.
Grid Interactivity
Gas-powered generators and solar generators work differently with the main power grid.
Gas generators are mainly for power outages. They usually don’t do much when there’s normal power and just sit around.

Solar generators need sunlight to work well. On sunny days, they make more power than needed. This extra power goes into batteries for later. It’s helpful at night or if the power goes out.
Also, when people aren’t using a lot of electricity, solar generators can take some power from the main grid to fill up their batteries. Then, when lots of people want electricity, and it costs more, you can use the power saved in the batteries. This helps cut down on electricity bills.
Which Type of Generator Do You Need?
Selecting the ideal power source relies heavily on the specific scenarios in which you anticipate needing backup power:
Scenario 1: When You Need Backup
When the grid goes down, a gas generator often makes the most sense for emergency home power. Gas generators deliver instant, high-wattage electricity on demand to run essentials like furnaces, fridges, medical devices, and lights. Their compact size takes up little space for storage.
Gas generators are inexpensive to purchase compared to solar alternatives. They provide continuous power for days with an adequate fuel supply, and basic mechanical skills allow easy setup and operation.
The main drawbacks are noise, toxic emissions, and dependence on fuel access in an emergency. But for short-term, high-power backup during multi-day blackouts, gasoline generators excel.
Scenario 2: When You’re Camping or Enjoying Outdoor Activities
For powering camping trips, outdoor events, or recreational vehicles, a portable power station that utilizes solar technology offers unique benefits over fuel generators. Their silent operation preserves nature’s sounds and won’t disturb others.
Solar generators recharge all day from the sun passively, producing free renewable electricity while you’re away. They avoid the need for transporting heavy, messy, flammable gasoline canisters.
Solar generators are emissions-free and eco-friendly. Their integrated batteries provide nights of use between charges. And they save money long-term over gasoline costs.

The limitations are lower power ratings that may require careful load planning. Dependency on sunny skies is also a downside, though manageable with proper generator sizing. Solar generators are hard to beat for clean, quiet, sustainable off-grid power.
Scenario 3: Jobsites and Work Areas
A gas-powered generator is often the best choice for construction sites or other heavy-duty work environments. Their ability to generate power on demand and for extended periods makes them ideal for tools and machinery. However, it’s essential to factor in the long-term fuel costs and harmful emissions they produce.
In comparison, a solar-powered generator might not offer the same raw power level but can be helpful for lighter tasks or in areas where noise or emissions are a concern. However, ensuring that your chosen powered generator fits the job’s needs is crucial.










