Can a Solar Generator Power a House?
Updated:

Probably the best departure point for answering this interesting question is to define exactly what a solar generator is. This is important because, in many people’s minds, a generator can power a house or even an entire industrial complex.
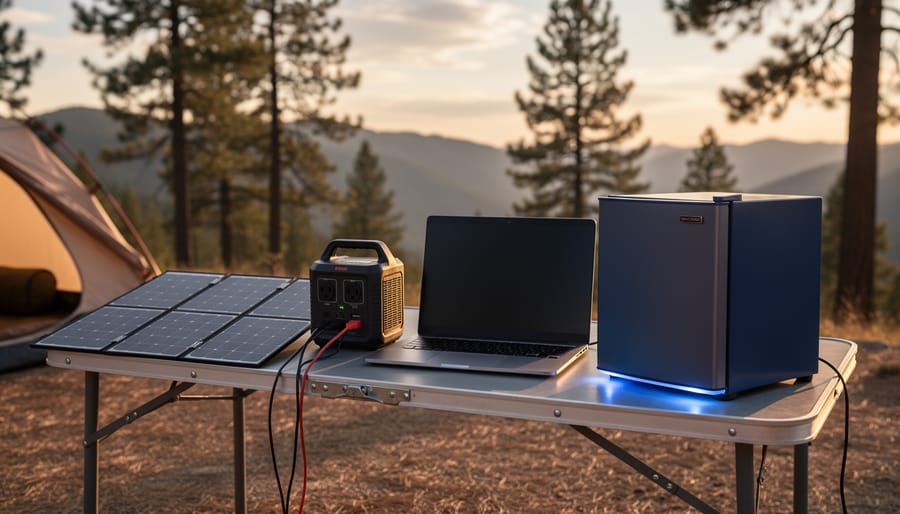
However, solar generators, or solar power stations as they are also known, are far less capable and limited in capacity. Essentially, solar generators are small portable devices used as modest power sources for use in remote locations.
Of course, this depends on the generator in question, but generally, they aren’t capable of large outputs. That doesn’t mean that they aren’t handy additions to any household’s backup power arsenals.
Unfortunately, in the vast majority of cases, the answer to the question is probably no. A solar generator could not realistically power an entire house. Let’s look at the realities of the situation to build a clear picture of why this is so.
What Exactly Is a Solar Generator?
Diesel or gas-powered generators are often large enough to power an entire hotel, hospital, or industrial plant. The caveat here is that there are a few limitations to the size and outputs of these units. The same applies to smaller, portable fossil fuel homes or industrial generators.
Solar generators, on the other hand, use solar panels to harvest solar energy which is then stored in solar batteries. This DC voltage generated by the solar panels is made available for use via a series of DC and USB outlets. In addition, most solar generators include an inverter which allows high voltage AC devices to also be used.
Solar generators range in size from fairly modest 300-watt models to far more robust 2,000-watt types. If you have good technical skills, it is also possible to build your own solar generator to match your exact needs. And harvesting a solar generator’s power you have built yourself is particularly satisfying.
What Are Solar Generators Typically Used for?
Generally, solar generators are used to supply power on camping, fishing trips, or when working away from AC power sources. For instance, a farmer could use a solar generator to run power tools in distant locations on the property.
Campers and hikers can also enjoy creature comforts while enjoying the peace and quiet of the outdoors using them. Unlike a gas-powered generator, they are totally quiet and unobtrusive. Solar generators are not limited to recreation or work applications though.
A capable solar generator can make a great addition to homeowners’ emergency equipment arsenals. This is an important role if there are family members that rely on medical support such as CPAP machines. Outside of that, freezers or fridges can be run off a solar generator reducing food spoilage during power outs.
In most cases, commercial solar generators consist of the generator assembly and a solar panel. If you roll your own, you can even integrate the generator and solar panel into a single unit. either way, it is never really necessary to install solar panels to specifically power the generator.
That said permanently installing solar panels or a single solar panel is not necessarily a bad thing. If fact, a permanent, dedicated solar panel may be a good idea. And it would be fairly easy to hook a permanent solar panel up to the generator. Either way, the solar variety will always trump gas generators in terms of green power generation.
So, Can a Solar Generator Power a House?
Unless the house is a very small cabin or a modest, tiny house or you use multiple solar generators, a solar generator can not power a house. Essential devices can be powered but generally, solar generators don’t have the capacity to reliably power an entire family household.
To put this into perspective, let’s look at the average power consumption figures for home appliances.
Appliance | Average Power Consumption in Watts |
Microwave oven | 1150 |
Washing machine | 450 |
Vacuum cleaner | 780 |
Electric iron | 1100 |
Computer | 50 |
TV | 110 |
Fridge | 80 |
Chest freezer | 300 |
Reading lamp | 35 |
Hair dryer | 800 |
Laptop | 35 |
Laser printer | 1100 |
HP air conditioner | 1500 |
Fluorescent light | 300 |
Electric heater | 2500 |
Table fan | 20 |
Considering these figures, even the largest solar generators could only run a couple of appliances at any one time. Any solar system large enough to power the entire house could not qualify as a solar generator. It would then, strictly speaking, be a domestic solar installation.
The Role of the Solar Generator in the Home
Because a solar generator can’t power the average home, doesn’t mean it can’t play an important domestic role. Outside of the obvious recreational and remote worksite applications, here are a few useful applications for solar generators. Most of which will form part of homeowners’ emergency backup power supply plans for power outages.
Powering:
- medical support devices
- fridges and freezers
- emergency lighting
- home surveillance and security devices during prolonged power outages
- automated gates and doors
And it’s in any situation where a prolonged lack of grid power hits you that the solar power generator is particularly handy. Emergency systems batteries will eventually run down if your power is going to be out for several days. A solar generator can charge the batteries during the day and run critical systems from those batteries at night. And that can be repeated indefinitely until they restore the municipal supply.
How to Choose a Solar Generator
This is certainly one of those “bigger is better” scenarios. A solar generator that is bigger than you really need is far better than one that is way too small. Of course, budget plays an important role, but try to get the biggest generator you can afford.
Sizing the Solar Panels and Generator
To get an idea of what size your generator should be, takes a bit of strong coffee and careful thought. A good jump-off point is making a list of all the critical devices and appliances that should be supported during a power outage.
List them in descending order of importance and be frugal — don’t include things that are not absolutely needed. Now the coffee and head-scratching come into play. You now need to calculate the total power consumption (in watts) of all those items combined.
Most electric devices and appliances will have an adhesive tag or printed bulletin on them that will list their operating voltage, amperage, and wattage. If they don’t, you can consult an online resource to find an average wattage for that type of appliance.
When you have added all the wattage ratings together, you’ll know the size of solar generator you will need. Always add a safety margin of around 25 percent to be on the safe side. For example, if your total wattage requirement is 2,500 watts, then you should look at a 3,000-watt generator.
One point to remember when choosing a generator is the capacity of the solar panels it ships with. Manufacturers will often include solar panels that are just capable of running the generator. It is often a good idea to include extra solar panels in the setup to ensure maximum efficiency.
In Closing
Even though you can’t run any but the smallest tiny home on a solar generator, they are great devices. They allow you to use tools or recreational devices far from power sources and can help a lot in brown or blackouts. And if you choose wisely when buying one, you’ll probably be surprised at how versatile they really are.
We hope this article has helped to clarify the capacity and function of solar generators. If you’d like to share any comments, advice, or additional information, please use the comments section below.