Your Dream Home Can Run on Pure Sunshine (Here’s How)
Updated:

Transform your home into a self-sustaining powerhouse that produces as much energy as it consumes. Zero-energy homes represent the pinnacle of sustainable living, combining advanced architectural design with cutting-edge renewable technology to eliminate utility bills while maximizing comfort. Through strategic implementation of benefits of solar energy, superior insulation, and smart home automation, these revolutionary dwellings are reshaping our approach to residential construction and energy consumption.
Modern zero-energy homes harness passive solar design, thermal mass materials, and high-performance windows to maintain optimal temperatures year-round without traditional heating and cooling systems. By integrating energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and advanced energy monitoring systems, homeowners can track and optimize their power usage in real-time. The result? A completely self-sufficient living space that protects both the environment and your wallet, while setting a new standard for sustainable architecture in the 21st century.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential components, design principles, and practical steps needed to achieve true zero-energy status for your home, whether you’re building from scratch or retrofitting an existing structure.

What Makes a Home Truly Zero Energy?
Energy Production vs. Consumption
Achieving true zero energy status requires a delicate balance between how much energy your home produces and consumes. Think of it like maintaining a bank account – your energy production needs to match or exceed your usage over the course of a year. From my experience helping homeowners achieve this balance, I’ve found that most homes require about 7-10 kW of solar capacity to offset their annual energy consumption.
The key is to first minimize your energy consumption through efficient appliances, proper insulation, and smart energy habits. Once you’ve reduced your usage, you can accurately size your solar system to meet those needs. I recommend tracking your energy consumption for at least three months to get a realistic picture of your needs.
Remember that energy production varies seasonally – you’ll likely produce excess energy in summer months and rely more on the grid during winter. This is where net metering comes in handy, allowing you to bank your excess production as credits for times when you’re consuming more than you produce. The goal isn’t to be off-grid completely, but rather to achieve net-zero consumption over the year.
Beyond Solar Panels
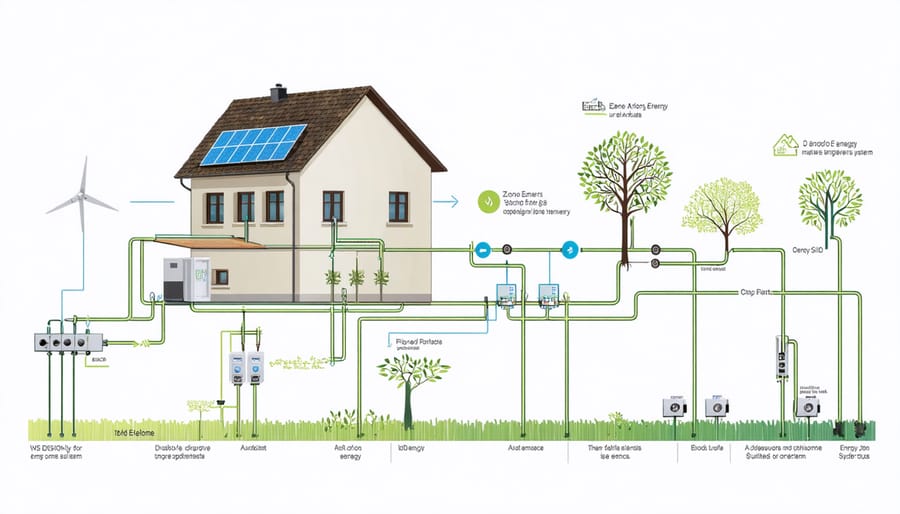
While solar panels are a cornerstone of zero-energy homes, achieving true energy independence requires a holistic approach. Your home needs a robust insulation system, starting with high-performance windows and doors that prevent heat loss. Advanced air-sealing techniques and proper ventilation systems, like heat recovery ventilators (HRV), help maintain indoor air quality while minimizing energy waste.
Smart home automation plays a crucial role too. Installing programmable thermostats, LED lighting, and energy-efficient appliances can reduce your baseline energy consumption by 30-40%. Don’t overlook the power of passive solar design – strategic placement of windows, thermal mass materials, and proper orientation of your home can naturally regulate temperature.
Water heating typically accounts for about 20% of home energy use, so consider solar thermal systems or heat pump water heaters. Energy storage solutions, like battery systems, help manage power during cloudy days and nighttime. Remember, every component works together – from the ground-source heat pumps for climate control to the energy-monitoring systems that help you track and optimize your usage. It’s this integrated approach that makes true zero-energy living possible.
Essential Components for Your Zero Energy Home
Solar System Sizing and Design
Let me share a practical approach to sizing your solar system that I’ve refined over years of helping homeowners achieve energy independence. First, gather your home’s annual electricity usage from your utility bills – this gives you a baseline for your energy needs. Typically, you’ll want to review 12 months of bills to account for seasonal variations.
To determine your solar array size, consider your solar system design requirements based on your location’s peak sun hours and energy consumption patterns. For example, if your home uses 10,000 kWh annually and your area receives 5 peak sun hours daily, you’ll need approximately 7-8 kW of solar capacity.
Don’t forget to factor in these key elements:
– Roof orientation and angle
– Available unshaded space
– Local climate conditions
– Future energy needs
– Battery storage requirements
I recommend using the “80% rule” – design your system to produce about 80% of your current usage, then implement energy-efficiency measures to reduce consumption. This approach often proves more cost-effective than oversizing your system.
For battery sizing, consider your critical loads and desired backup duration. A typical home might need 10-15 kWh of storage capacity to maintain essential functions during outages. Remember to check local regulations and utility requirements before finalizing your design.
Energy Storage Solutions
When it comes to achieving true zero-energy living, effective energy storage is crucial. Modern battery systems have revolutionized how we store and use solar power, making it possible to keep your home running smoothly even when the sun isn’t shining.
The heart of most home energy storage systems is the lithium-ion battery bank. These batteries have become increasingly affordable and efficient, with popular options like the Tesla Powerwall and LG Chem RESU leading the market. A typical system for a family home usually requires 10-15 kWh of storage capacity, though your specific needs may vary based on energy consumption patterns.
I recently helped a friend install a hybrid system that combines traditional battery storage with a clever water heating solution. By using excess daytime solar production to heat water, they created a thermal battery that provides both hot water and home heating during cloudy days.
For backup power, many homeowners opt for a combination approach. While batteries handle daily energy storage, having a small backup generator can provide peace of mind during extended periods of bad weather or emergencies. Smart energy management systems help optimize this setup by automatically prioritizing stored energy use and managing power distribution throughout your home.
Remember to consider future expansion when planning your storage system. Starting with a modular battery solution allows you to add capacity as your needs grow or as technology improves.
Smart Energy Management
The heart of a zero-energy home lies in its smart energy management systems. Think of these systems as your home’s energy brain, constantly monitoring and optimizing power usage to maintain the perfect balance between consumption and production.
Modern smart home systems use sensors and real-time monitoring to track energy usage across different appliances and systems. You can view this data through user-friendly apps on your smartphone, making it easy to spot energy-hungry appliances or unusual consumption patterns. I remember installing my first energy monitor – it was eye-opening to see how much power my old refrigerator was consuming!
The key to optimization is automation. Smart thermostats learn your schedule and adjust heating and cooling accordingly. Motion sensors ensure lights aren’t left on in empty rooms. Even your appliances can be programmed to run during peak solar production hours when your panels are generating the most power.
Load shifting is another clever strategy. This involves scheduling energy-intensive tasks like laundry or dishwashing during sunny hours. Many smart systems can now automatically trigger these appliances based on your solar production levels.
For best results, combine these technologies with good old-fashioned energy-saving habits. Regular monitoring helps you stay on track with your zero-energy goals while identifying new opportunities for optimization. The data collected over time becomes invaluable for making informed decisions about future energy improvements.
Making It Happen: Practical Steps
Assessment and Planning
Creating a zero-energy home starts with a thorough assessment of your current energy usage and property characteristics. Begin by tracking your household’s energy consumption over several months to establish a baseline. This includes reviewing utility bills and noting seasonal variations in usage patterns.
Next, evaluate your property’s potential for renewable energy generation. Consider factors like roof orientation, sun exposure throughout the year, and any potential shading from trees or neighboring structures. A south-facing roof typically offers optimal conditions for solar panel installation in the Northern Hemisphere.
You’ll also need to assess your home’s energy efficiency. Look for areas of improvement such as insulation, air sealing, window quality, and HVAC system efficiency. Sometimes, simple upgrades can significantly reduce your energy needs before implementing renewable solutions.
Create a detailed plan that includes both immediate and long-term goals. Consider your budget, available incentives, and local building codes. Remember that achieving zero energy status often happens in stages, so prioritize improvements based on their impact and cost-effectiveness. Working with an energy auditor can provide valuable insights and help create a more targeted approach to your zero-energy journey.
Installation and Integration
Transforming your home into a zero-energy dwelling involves several key implementation phases that require careful planning and execution. From my experience helping homeowners make this transition, I’ve found that starting with a comprehensive energy audit is crucial. This initial assessment identifies your current energy usage patterns and potential improvement areas.
The next phase focuses on improving your home’s envelope through proper insulation, sealing air leaks, and installing energy-efficient windows. These foundational improvements significantly reduce your energy needs before adding renewable systems.
Once your home is properly sealed and insulated, it’s time to install your renewable energy systems. While many DIY enthusiasts can handle basic preparations, I always recommend working with a professional solar installation team for the electrical components. They’ll ensure your system meets local codes and operates safely.
The integration phase includes setting up monitoring systems and smart home controls. These tools help you track energy production and consumption in real-time, allowing you to optimize your usage patterns. I’ve found that most homeowners can handle this part themselves with some basic technical knowledge.
Finally, commissioning and testing ensure all systems work together efficiently. This phase typically takes about two weeks, during which you’ll learn to operate your new zero-energy home systems and make any necessary adjustments.
Maintenance and Optimization
Keeping your zero energy home running at peak efficiency requires regular attention and fine-tuning. Start with routine solar panel maintenance, including cleaning the panels every 3-4 months and checking for any debris or damage. I’ve found that a simple mixture of water and mild soap works wonders for keeping panels clean and efficient.
Monitor your home’s energy management system regularly to spot any unusual patterns in consumption or production. Many of my DIY enthusiasts set monthly reminders to review their system’s performance data. This helps identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Don’t forget about your home’s insulation and weatherstripping – these need annual inspection and occasional replacement. Check windows and doors for drafts during changing seasons, and refresh your HVAC filters monthly. Smart thermostats should be recalibrated seasonally to maintain optimal performance.
Remember to update your home automation settings as seasons change. Small adjustments to lighting schedules and temperature controls can make a big difference in overall efficiency. Consider keeping a maintenance log to track patterns and schedule regular check-ups.
Real-World Cost Analysis
Let’s break down the real costs of achieving a zero-energy home, based on my experience helping homeowners make this transition. The initial investment typically ranges from $30,000 to $60,000 beyond traditional construction costs, but don’t let that number scare you away – the long-term solar energy investment returns make it worthwhile.
The biggest expense usually comes from solar panel installation ($15,000-$25,000) and enhanced insulation ($8,000-$12,000). High-efficiency HVAC systems add another $10,000-$15,000, while energy-efficient windows and doors typically cost $5,000-$8,000. Smart home technology for energy management runs about $2,000-$3,000.
However, the savings are substantial. Most homeowners see their monthly energy bills drop to near zero, saving $1,500-$3,000 annually depending on location and previous energy usage. Factor in federal tax credits (currently 30% of solar installation costs) and state incentives, and the initial investment becomes more manageable.
Let’s look at a typical ROI scenario: With average energy savings of $2,400 per year and available tax incentives, most homeowners break even within 8-12 years. After that, it’s all savings. Plus, zero-energy homes typically command a 4-10% premium when sold, adding significant resale value.
One of my clients, Sarah, transformed her 2,000-square-foot home into a zero-energy dwelling last year. Her total investment was $45,000, but after tax credits and incentives, her out-of-pocket cost was $31,500. She’s now saving $2,800 annually on energy bills and expects to recoup her investment within nine years.
Remember, costs vary significantly based on location, home size, and existing infrastructure. I always recommend getting multiple quotes and checking local incentives before starting your project. The key is to view this as a long-term investment in both your home’s value and environmental sustainability.
Creating a zero-energy home isn’t just about saving money or reducing your carbon footprint – it’s about being part of a sustainable future that benefits everyone. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components of achieving a zero-energy home, from proper insulation and efficient appliances to solar panel installation and smart energy management systems.
Remember, every step you take toward energy independence matters, whether you’re starting with simple energy-efficient upgrades or planning a complete zero-energy build. The initial investment might seem substantial, but the long-term benefits – both financial and environmental – make it worthwhile.
As someone who’s helped countless homeowners on their journey to energy independence, I can tell you that the satisfaction of producing all the energy you need is incredible. Start by conducting an energy audit of your home, then create a realistic plan that fits your budget and timeline. Consider joining local sustainability groups or online communities where you can share experiences and learn from others who’ve already made the transition.
The path to a zero-energy home is more accessible than ever, thanks to advancing technology and decreasing costs. Take that first step today – whether it’s upgrading your insulation, installing LED lighting, or consulting with a solar professional. Your future self (and the planet) will thank you for it.