Build Your Perfect Solar Setup with This Power System Calculator
Updated:

Calculate your ideal solar system size in minutes instead of hours with a reliable solar power calculator – the essential first step that separates successful installations from costly mistakes. Whether you’re planning your first off-grid cabin setup or upgrading your home’s existing solar array, accurate system sizing determines everything from battery capacity to panel configuration. Our interactive solar calculator helps you precisely match your energy needs with the right equipment, factoring in local sun hours, energy consumption patterns, and seasonal variations.
Think of a solar calculator as your financial safety net: it prevents over-purchasing expensive equipment while ensuring your system can handle peak demands. By entering your specific power requirements, location data, and budget constraints, you’ll receive customized recommendations that optimize your investment. The difference between guessing and calculating can mean thousands of dollars saved and years of reliable renewable energy production.
Ready to start planning your solar journey? Let’s dive into how our calculator can transform complex solar calculations into clear, actionable steps that ensure your system meets your exact needs, while helping you avoid the common pitfalls that plague DIY solar installations.
Why You Need a Solar Power Calculator
Common Solar Sizing Mistakes
Let me share a few eye-opening cases I’ve encountered where incorrect calculations led to system failures. Just last summer, I helped a client who had sized their system based only on their current energy usage, completely forgetting about their planned electric vehicle purchase. Within months, their system was struggling to keep up with demand.
Another common mistake I see is underestimating seasonal variations. A family in Minnesota sized their system using summer sunlight hours, only to find themselves with insufficient power during the shorter winter days. They had to add extra panels at considerable expense.
Battery backup sizing is another critical area where mistakes happen. One off-grid enthusiast calculated their storage needs for a single day, not accounting for consecutive cloudy days. This led to frequent power outages during a particularly rainy week.
Perhaps the most costly mistake I’ve witnessed was ignoring voltage drop in long cable runs. A mountain cabin installation lost nearly 20% of its generated power due to improper wire sizing, requiring a complete system redesign.
These real-world examples highlight why accurate calculations are crucial for a successful solar installation.
Benefits of Using a Calculator
Using a solar power system calculator takes the guesswork out of your solar journey and provides numerous advantages over rough estimations. First and foremost, it helps you avoid the costly mistake of under-sizing or over-sizing your system. By inputting specific details about your energy needs and location, you’ll get precise calculations that match your unique situation.
These calculators factor in variables that might not immediately come to mind, such as seasonal variations in sunlight, panel efficiency losses over time, and your local climate conditions. This comprehensive approach ensures you’re working with realistic numbers rather than optimistic assumptions.
I remember when I first started planning my solar setup – I was way off in my manual calculations until I used a proper calculator. It saved me from buying several extra panels I didn’t actually need, resulting in significant cost savings.
Additionally, a good solar calculator helps you understand your return on investment by providing detailed financial projections. It can estimate your energy savings, calculate potential tax incentives, and show you exactly how long it will take for your system to pay for itself. This data-driven approach gives you the confidence to move forward with your solar project, knowing you’ve made well-informed decisions based on reliable calculations.

Essential Components to Calculate
Load Requirements
Before diving into solar calculations, you’ll need to determine your daily power requirements. Start by creating a list of all electrical devices you plan to power with your solar system. For each device, locate the power rating (usually in watts) on the device label or manual.
I learned this the hard way when I first started – I forgot to include my garage door opener and had to upgrade my system later! To make this process easier, multiply each device’s wattage by the number of hours you use it daily. For example, a 60-watt light bulb used for 5 hours equals 300 watt-hours per day.
Don’t forget about seasonal variations. Air conditioners in summer or heaters in winter can significantly impact your calculations. Also consider any future additions to your power needs, like an electric vehicle charging station.
For accuracy, I recommend monitoring your actual electricity usage for a month. Most utility bills show your daily consumption, which can serve as a reliable baseline. Add about 20% to your total as a safety margin – this accounts for system inefficiencies and ensures you won’t fall short during peak usage times.
Solar Panel Sizing
To determine the right size for your solar panel system, you’ll need to consider several key factors. Start by calculating your daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh) – I learned this the hard way when I initially undersized my first system! Once you have your daily usage, factor in the average peak sun hours in your location. Our solar panel sizing calculations take these variables into account, along with system efficiency losses typically ranging from 20-25%.
For example, if your daily energy needs are 5000Wh and you receive 5 peak sun hours, you’ll need at least 1250W of solar panel capacity (accounting for losses). Remember to consider factors like shading, panel orientation, and seasonal variations. I always recommend adding a 20% buffer to your calculations to ensure your system can handle unexpected increases in energy consumption or decreased solar production during cloudy periods.
Battery Bank Capacity
When sizing your battery bank, you’ll need to carefully consider your daily energy needs and desired backup duration. Start by calculating your total daily power consumption in watt-hours (Wh), then factor in additional capacity for cloudy days and system inefficiencies. Choosing the right solar battery involves understanding both capacity and depth of discharge (DoD) ratings.
I always recommend adding a 20% buffer to your calculated capacity needs – trust me, you’ll appreciate that extra cushion during extended periods of low sunlight! For most home systems, you’ll want enough storage to cover 2-3 days of typical usage. Remember that proper battery storage management is crucial for maximizing battery life and system efficiency.
To calculate your battery bank size in amp-hours (Ah), divide your daily energy requirement by your battery bank’s voltage (typically 12V, 24V, or 48V). For example, if you need 5000Wh daily with a 24V system, you’d need at least a 208Ah battery bank (5000Wh ÷ 24V = 208Ah).

Using Our Solar Calculator
Input Your Requirements
Let’s get your solar calculator journey started by entering the right data – this is where the magic begins! First, make a list of all your electrical appliances and devices. I remember when I first did this, I almost forgot my garage door opener, which would have thrown off my calculations completely!
For each device, you’ll need two key pieces of information: its power rating (in watts) and daily usage hours. Check the label or manual for the wattage – it’s usually printed right there. Can’t find it? Most common appliances have standard ratings you can look up online.
Next, enter your daily usage pattern. Be realistic here! If you run your air conditioner for 6 hours during summer but barely use it in winter, factor in these seasonal variations. This helps you calculate battery capacity requirements accurately.
Pro tip: Don’t forget about those energy-hungry appliances that run occasionally, like washing machines or power tools. Even though they’re not used constantly, they can significantly impact your system’s size requirements.
Include any future additions you’re planning – maybe an electric vehicle charging station or a new hot tub? It’s better to slightly overestimate than underestimate your needs. Remember, we’re building a system that should serve you well for many years to come!
Keep your usage data handy – you’ll need these numbers for the next steps in sizing your solar power system.
Understanding the Results
Let’s dive into what those calculator numbers mean for your solar journey. When you input your data and hit that calculate button, you’ll receive several key pieces of information that will shape your solar system design.
First, you’ll see your recommended system size in kilowatts (kW). This number tells you how much solar power capacity you’ll need to meet your energy goals. For example, if the calculator suggests a 6kW system, that means you’ll need about 20-24 solar panels, depending on their individual wattage.
The calculator will also show your estimated daily energy production. I remember when I first calculated mine – I was surprised to learn my roof could generate more power than I initially thought! This number helps you understand if the system will meet your household’s needs throughout the year.
Pay special attention to the battery storage recommendations if you’re planning an off-grid system. The calculator typically provides this in kilowatt-hours (kWh), representing how much energy you should be able to store for nighttime use and cloudy days.
The financial section is particularly enlightening, showing your estimated initial investment and potential savings over time. Don’t be alarmed by the upfront costs – focus on the return on investment (ROI) timeline, which usually ranges from 5-10 years depending on your location and energy usage.
One often overlooked output is the roof space requirement. This tells you how much area you’ll need for panel installation. If the suggested space exceeds your available roof area, you might need to consider alternative mounting locations or higher-efficiency panels.
Remember that these results are estimates based on your inputs and local solar data. It’s always wise to verify these numbers with a local solar professional, especially if you’re planning a DIY installation. They can help you account for specific factors like shading or local regulations that online calculators might not consider.
Real-World Application Examples
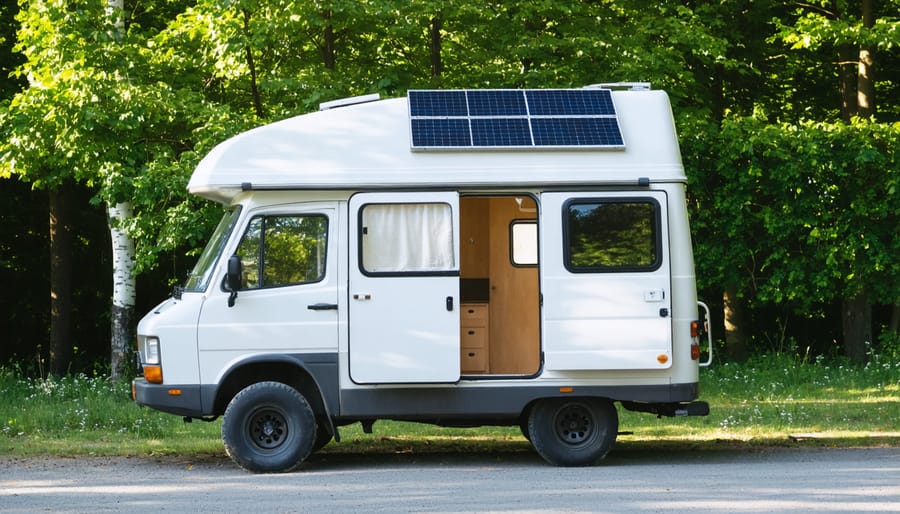

Van Life Setup
Let’s walk through a real-world example of sizing a solar system for a camper van. I recently helped my friend Sarah calculate her power needs for her weekend warrior van setup, and it’s a perfect illustration of how to use our calculator.
Sarah’s basic power requirements included:
– 12V refrigerator (40W, running 12 hours/day)
– LED lights (20W total, 4 hours/day)
– Laptop charging (65W, 3 hours/day)
– Mobile devices (25W, 4 hours/day)
– Small inverter losses (10% overhead)
Plugging these numbers into our calculator:
Daily Energy Usage = (40W × 12h) + (20W × 4h) + (65W × 3h) + (25W × 4h) = 755Wh
Adding 10% for inverter losses = 830Wh per day
For a typical van setup in varying weather conditions, we recommend having 2-3 days of autonomy. Sarah opted for two 100Ah 12V lithium batteries (2,400Wh total capacity) and 400W of solar panels on her roof. This gives her plenty of buffer for cloudy days and ensures she can run her system year-round, even during shorter winter days.
The setup has worked beautifully for Sarah’s weekend trips, and she’s even managed several week-long adventures without any power issues. Remember, your specific needs might differ, but this example shows how simple calculations can lead to a reliable system.
Off-Grid Cabin
Let’s walk through a real-world example of sizing a solar system for a cozy off-grid cabin. I recently helped my friend Sarah calculate the perfect setup for her weekend getaway in the mountains, and it’s a great illustration of how our calculator works.
Sarah’s cabin has basic power needs: LED lighting, a small refrigerator, laptop charging, and a few small appliances. After listing her devices, we determined her daily energy consumption was approximately 2.5 kWh. Using the calculator, we factored in:
• Average daily sun hours in her location (5 hours)
• System losses (20%)
• Two days of backup power for cloudy weather
• Battery depth of discharge (50%)
The calculator recommended a 1.2 kW solar array (typically 4-5 panels) and a 400Ah battery bank. While this might seem small compared to complete solar backup systems for full-time homes, it’s perfect for weekend cabin use.
Sarah’s total investment was around $3,000, including panels, batteries, charge controller, and inverter. She’s now enjoying reliable power while keeping her carbon footprint minimal. This example shows how proper sizing can create an efficient, cost-effective solution for small off-grid applications.
Remember, your specific needs might differ, but the calculation process remains the same. Start with your daily usage and let the calculator guide your component selection.
Taking the first step toward solar power can feel overwhelming, but with the right calculations and planning, you’re already on the path to energy independence. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components of sizing your solar power system, from understanding your energy needs to factoring in environmental conditions and battery storage requirements.
Remember, a solar power calculator isn’t just a convenience – it’s your safeguard against costly oversizing or undersizing mistakes. By taking the time to input accurate data about your energy consumption, local weather patterns, and available installation space, you’re setting yourself up for long-term success with your solar project.
As someone who’s helped countless DIY enthusiasts plan their solar setups, I can’t stress enough how important it is to double-check your calculations. Don’t rush this process – take a weekend to gather your utility bills, measure your roof space, and research local solar regulations. The effort you put into planning now will pay dividends in system efficiency and cost savings later.
Start small if you’re feeling uncertain. Calculate the requirements for a single room or specific appliances first. This approach helps you build confidence while learning the intricacies of solar sizing. As you become more comfortable with the calculations, you can gradually expand your system design to cover more of your energy needs.
The solar community is incredibly supportive, and there’s no shame in asking for help or having someone review your calculations. Share your plans with fellow enthusiasts, join online solar forums, and don’t hesitate to consult with local solar professionals if you need additional guidance.
Ready to begin? Fire up that calculator and start plugging in your numbers. Whether you’re planning a small backup system or dreaming of taking your entire home off-grid, proper sizing calculations are your foundation for success. Remember, every solar journey starts with a single calculation – and you’ve now got the tools to make it count.